New Year’s resolutions will bring questions about weight loss meds.
Explain that weight loss meds aren’t a “magic bullet.”
Emphasize lifestyle changes first. Then consider adding a med for patients with a BMI of 30 or more...and 27 or more with a weight-related condition, such as diabetes.
Expect injectable tirzepatide or semaglutide to be in the spotlight...since they seem most effective. But anticipate that many patients will try an Rx oral med first...due to cost and availability.
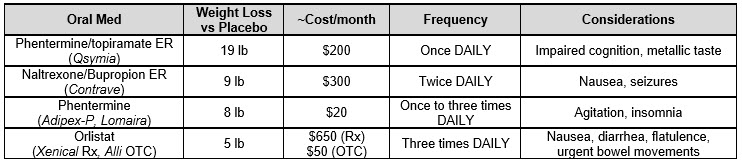
Help guide med choice. Tailor based on weight loss goals, comorbidities, side effects, etc.
For instance, avoid phentermine-containing meds in patients with a history of CV issues or anxiety.
And don’t recommend naltrexone/bupropion for patients taking opioids...due to its naltrexone component.
Be aware of dispensing considerations.
For example, phentermine/topiramate has a REMS program due to the risk of birth defects. And phentermine-containing meds are C-IVs.
Recommend starting weight loss meds with low doses...and titrating as tolerated...to help limit side effects.
Keep in mind that oral meds should generally be stopped if the patient doesn’t lose at least about 5% of their body weight after 12 weeks on a maximum dose.
Steer patients away from OTCs or supplements promoted for weight loss. Many contain a mix of caffeine, vitamins, or herbals...all of which have conflicting evidence of efficacy.
Encourage patients to join a weight loss support group. Data suggest that patients who join a group lose more weight...and keep it off longer.
Use our resource, Weight Loss Products, for more on other options.
- Grunvald E, Shah R, Hernaez R, et al; AGA Clinical Guidelines Committee. AGA Clinical Practice Guideline on Pharmacological Interventions for Adults With Obesity. Gastroenterology. 2022 Nov;163(5):1198-1225.
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK). Prescription Medications to Treat Overweight & Obesity. March 2023. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/weight-management/prescription-medications-treat-overweight-obesity (Accessed November 10, 2023).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Overweight & Obesity. September 21, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/index.html/ (Accessed December 5, 2023).
- Medication pricing by Elsevier, accessed Dec 2023.

